Tarrifs
As history has repeatedly proven, one trade tariff begets another, then another - until you’ve got a full-blown trade war. No one ever wins, and consumers always get screwed.
- Mark McKinnon
Tarrifs Explained
Tarrif: a levy or duty that a government imposes on imported goods. It is a type of tax on goods when they are brought into the country from abroad. A tariff is different from other taxes like sales, income and property taxes. Tariffs directly affect the price of imported goods, which can lead to higher consumer prices and can alter trade dynamics and international relations. (Rodney Sullivan, Mayo Center of Asset Management)
Impact of Tarrifs
The tariffs are DESIGNED to create economic hardship. Why? So that Trump has a straight face rationale for releasing them, business by business or industry by industry. As he adjusts or grants relief, it’s a win-win: the economy improves and dissent disappears.
- Chris Murphy
This isn’t economic policy. It’s a weapon
- Tariffs cause widespread panic and pain
- Trump can relieve certain companies from tariffs as a form of extortion
- Slowly over time he will win over companies loyalty or else blackmail them in tariffs
Impact by Country
Canada
- Petroleum - cost of gas
- Automobiles - Cars themselves and the parts for replacing
- Lumber for building houses and buildings
China
- Manufactured goods - Almost all house hold goods
- Food - vegetables, spices, snack foods, vitamins
- Factory labor - Many American companies have factories in China, but it will not necessarily come back to the US at risk of expense to reopen
Mexico
- Fresh produce and vegtables
- Food - vegetables, spices, snack foods, vitamins
- Factory labor - Many American companies have factories in China, but it will not necessarily come back to the US at risk of expense to reopen
The Budget Lab at Yale University estimates that the U.S. consumer price level may rise by 2% this year, the equivalent of $3,000 per average household.
The Retaliation
American tarrifs do not only impact our economy, but they directly effect policy in the other country. China and Canada have already responded by announcing or threatening their own tarrifs against US goods. This will inturn pass the price increase to the consumer which will decrease international sales. Overall, tarrifs decrease trade on both sides.
History of Tarrifs
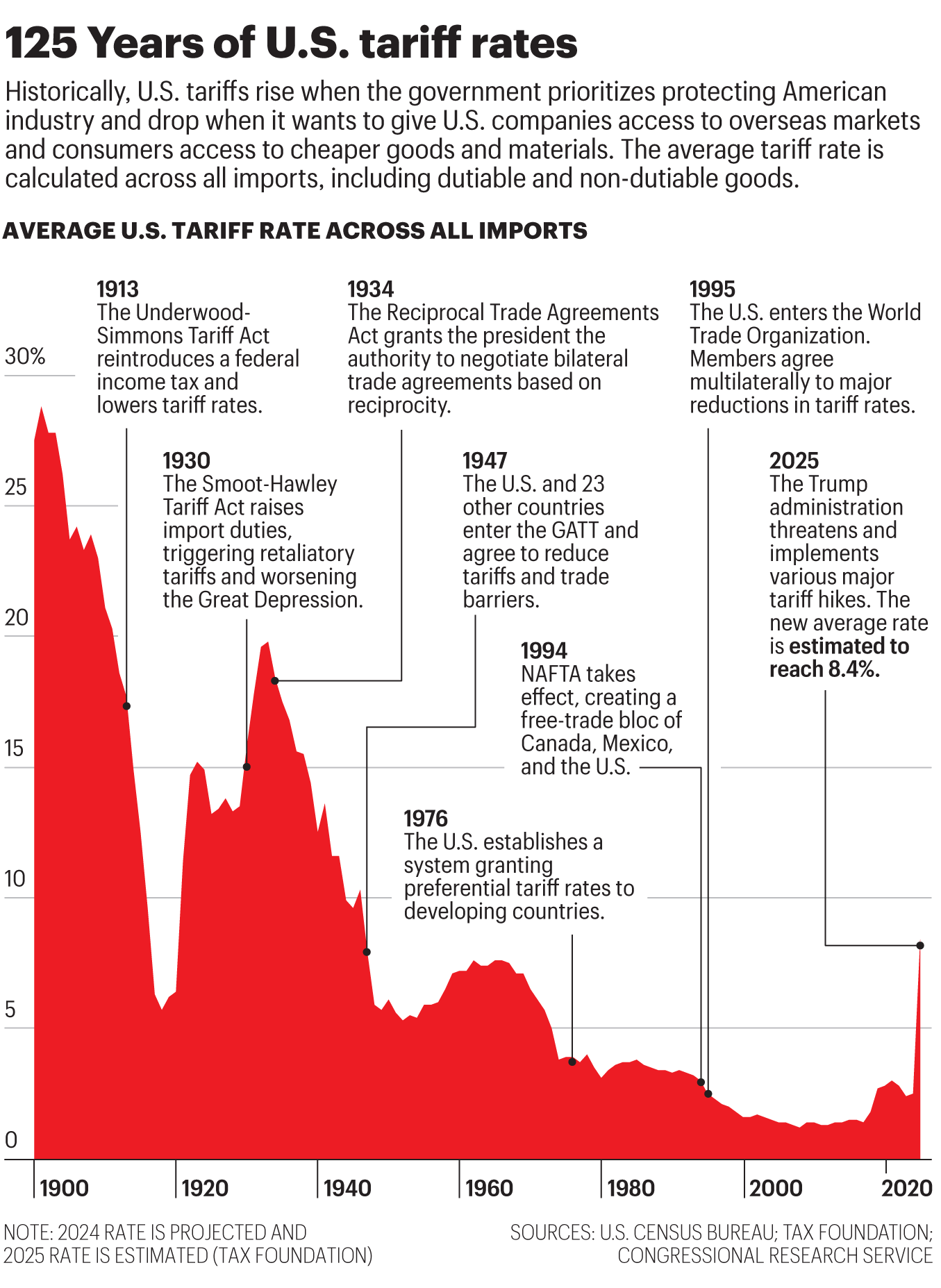
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
This is the precursor to the World Trade Organization that was established in 1947. This legal agreement stated that trade barriers were not beneficial to countries and that each country grows through trade. This agreement came into effect after the impacts seen by the great depression and WWII.
Even in the most successful cases of tarrifs, we do not see economic growth in the way that Trump is claiming it can accomplish. In the Smoot-Hawley Tarrif Act of 1930, only 1.4% of the GDP was affected. Currently trump is claiming his tariffs will affect 5%.
Responses and Survival
How Comapnies Will Respond
- Expect to see a slow down in production and expansion. Companies will want to play it safe amidst all the uncertainty.
- Bribery and "kissing the ring" will be the best way to convince the president to let their company bypass tarrif expenses. Companies will want to show support to the Trump administration and may show symbolic gestures of support like eliminating DEI programs.
How Individuals Will Responde
- Investors will shift over to more secure assets like gold instead of equity in companies.